7.9 External quality control
External control of the analytical results aims at providing an independent means to evaluate the quality of the results. The analysis of unknown samples as part of proficiency test exercises (PT) is an effective way of proving the quality of the results. The results reported by the participating laboratories are often evaluated by the PT organizers using the z and u scores.
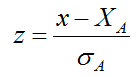
where x is the result reported by the participant laboratory and, XA and σA are the assigned value and the target standard deviation for the result, determined from the certified property value of the analysed material.
z-scores are meant to account for the trueness of the result. Assuming that appropriate values for XA and σA have been used and that the underlying distribution of analytical errors is normal, apart from outliers, in a well-behaved analytical system z-scores would be expected to fall outside the range –2 ≤ z ≤ 2 in about 4.6% of instances, and outside the range –3 < z < 3 only in about 0.3%.
u-scores are calculated as:
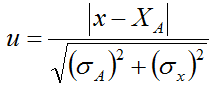
where the symbol 'σx' denotes the standard uncertainty of the submitted result x. If the assumptions
about XA and σA and about the normality of the underlying distributions are correct,
and the laboratory estimate of σx takes into account all the significant sources of uncertainty,
the u-scores would have a truncated normal distribution with unit variance. In a well-behaved analytical system only 0.1% of
u-scores would fall outside the range u < 3.29.
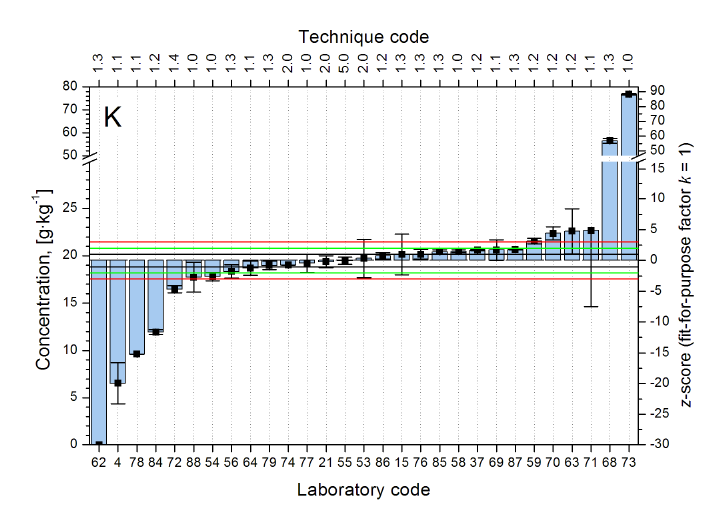
The IAEA Nuclear Science and Instrumentation Laboratory (NSIL) organizes proficiency test exercises periodically. The reports are published in the IAEA Analytical Quality in Nuclear Application Series. An example can be found at the IAEA publications website. Information for participation can be requested from IAEA Official Email.