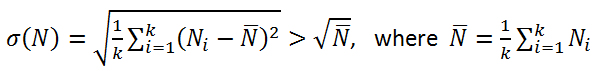7.5 Precision
Precision is the closeness of agreement between indications or measured quantity values obtained by replicate measurements
on the same or similar objects under specified condition. In EDXRF, the precision of a measurement with a result of N counts is
influenced by the statistics nature of counting process 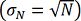 . Therefore, precision in the determination of the element
weight fraction wi is directly proportional to the square root of the measurement time tmeas and to the instrumental sensitivity Si .
It is also evident that the relative precision improves with the increase in elemental weight fraction wi.
. Therefore, precision in the determination of the element
weight fraction wi is directly proportional to the square root of the measurement time tmeas and to the instrumental sensitivity Si .
It is also evident that the relative precision improves with the increase in elemental weight fraction wi.
The overall precision can also include the contribution of other experimental factors (differences in sample positioning, stability of excitation flux intensity, among others) and must be assessed as the standard deviation σ(N) of k replicate measurements Ni rather than relying only on that arising from the counting statistics itself.