5.1.4 Particle induced x-ray emission (PIXE)

The measurement chambers in Ion Beam analysis dedicated stations in particle accelerators usually include multiple detectors for different Ion Beam analysis techniques, including PIXE, Particle Induced Gamma Emission (PIGE) and Rutherford Backscatter Spectrometry (RBS).
For high energies in the order of a few MeV the x-ray production cross section is proportional to Z12Z2-4, where Z1 refers to the atomic number of the ion, Z2 to that of the target atom.
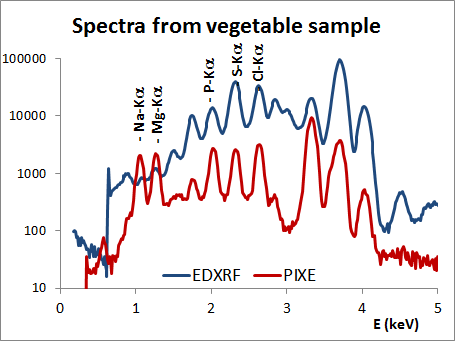
Opposite to the case of XRF, where the excitation radiation penetrates deeper than the effective thickness that the characteristic emission can travel, in the case of PIXE the penetration of the particles in the sample is limited to a few microns below the sample surface, thus limiting the technique to near surface analysis.
The cross sections for PIXE are higher for low and medium atomic number elements, and better detection limits are obtained, as compared to XRF. PIXE is routinely used for the analysis of elemental composition of air particulate matter (APM) collected on membrane filters in environmental studies.