2.4.1 Production of continuous radiation
Continuous x-rays are produced when electrons or other charged particles interact with the Coulomb field of the atoms while travelling through the matter. As a result of this interaction the electrons lose energy and decelerate. The energy lost by the electrons is emitted as x-rays photons, which can have variable energies, up to the maximum initial energy of the electron. This continuous radiation can be referred to as breaking radiation or Bremsstrahlung.
The probability of Bremsstrahlung emission is roughly proportional to
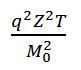
where q is the particle charge in units of electron charge e, Z is the atomic number of the material, T is the particle kinetic energy and M0 is the rest mass of the particle.
