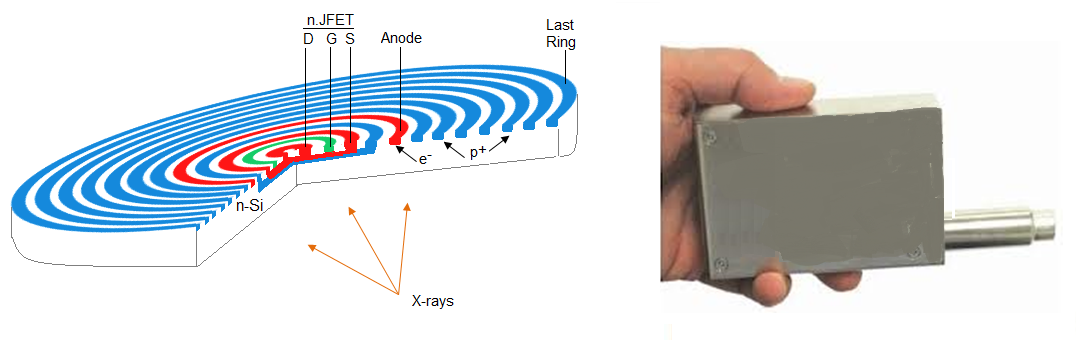
3.2.6.3 SDD
The SDD consists of a high-resistivity silicon chip featuring sequential sensitive elements from which the produced charge (electrons) is driven to a small collecting anode. The advantages of such arrangement are: a very short time for charge collection (allowing utilizing shorter processing times and very high input count rate) and the extremely low capacitance of its anode, leading to a very low electronic noise (improved energy resolution). Benefits of the SDD include:
- High count rates and processing
- Better resolution than traditional Si(Li) detectors at high count rates
- Lower charge collection time (time spent on processing X-ray event)
Because the capacitance of the SDD chip is independent of the active area of the detector, much larger SDD chips can be utilized (40 mm2 or more). This allows for even higher count rate collection ad increasing the overall geometry efficiency.