3.1.4 Charged particles
X-rays can also be produced by fast protons or other positive charged ions. Particle-induced X-ray emission (PIXE) is widely used for elemental analysis, and Particle Accelerators commonly dedicate a beam line for Ion Beam analysis (IBA).
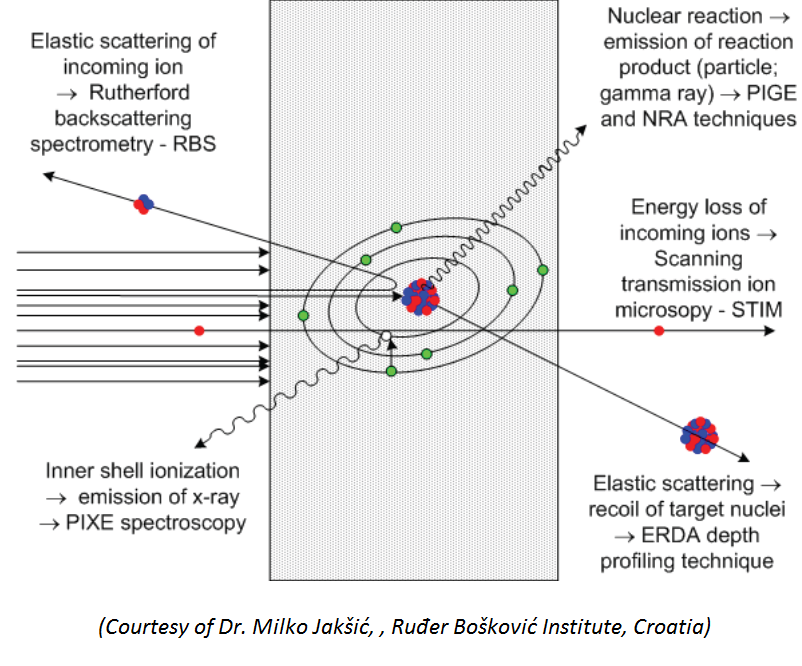
Excitation with charged particles induces some modifications in the materials.
Initially, a heavy moving particle loses energy in small steps through interactions with the electrons in the material through which it passes. Once the heavy particle loses enough energy such that it no longer has sufficient energy to excite an electron, then the particle loses energy by nuclear collisions. As the particle slows, it captures electron(s) to form a neutral atom (e.g., a proton becomes hydrogen, and an alpha forms helium). As a result hydrogen or helium impurities are created when a proton or an alpha particle, respectively, becomes neutralized in the material of passage.
Atoms can also be displaced from their normal position in the structure of the material; displacement atoms may leave lattice vacancies and lodge in interstitial locations or cause interchange of dissimilar atoms in the lattice structure. Large energy release in a small volume might also result in thermal heating of the material.